The “energy” in energy drinks and energy shots comes from two sources: caffeine (including the caffeine in guarana, yerba mate, and kola nut) and glucose, or sugar. The following ingredients are also common in energy drinks and “dietary supplement” products.
Taurine
Taurine is an amino acid, obtained in meats and fish, and helps regulate water and mineral salt levels in the blood. Studies on rats suggest caffeine and taurine have a synergy, enhancing caffeine’s stimulant properties, but not enough research on humans has been done. European nations once banned Red Bull out of concern over taurine’s safety, but continued research has not shown any ill effects. Taurine is not included on the FDA’s GRAS list (generally regarded as safe). At best, taurine’s impact in energy drinks is unknown.
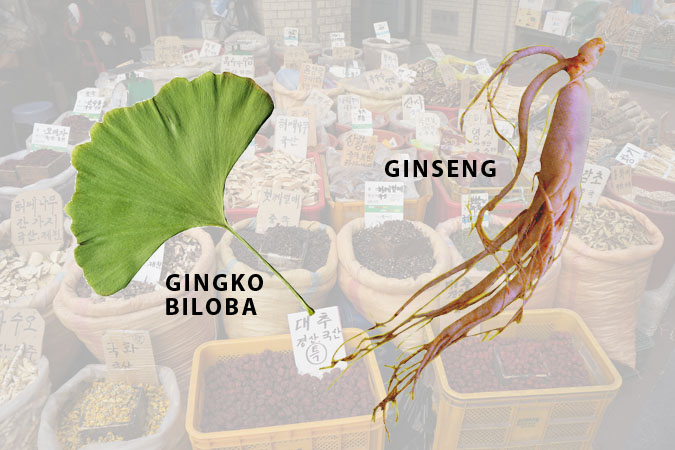
Ginseng
Ginseng is an herb. Traditional herbalists say it enhances mental wellbeing, boosts the immune system, and improves stamina. In energy drinks, ginseng probably won’t improve athletic performance. One study did show 200 mg of ginseng gave cognitive test-takers a mental boost, but only at that dose. Ginseng is shown to lower blood glucose and may interact with blood-thinning drugs like wayfarin, so consumers should consult their doctor before use.
Inositol
Inositol is a nutrient found in plants and animals that plays a role in brain, heart, muscle, and nerve cell functions. Insufficient evidence exists to support functional claims in dietary supplements, and quantities in energy drinks are too small to make an impact. The FDA lists it as “generally regarded as safe.”
B Vitamins
B vitamins help regulate metabolism, convert food to energy, and include thiamin, niacin, riboflavin, and cobalamin among others. They’re also believed to help maintain mental function. People get plenty of B vitamins in a normal diet, and excess is usually flushed from the system. But some amounts can be unsafe. B-6 is known to cause numbness and nerve damage in hands and feet when taken in large quantities over time. The FDA recommends 1.3 mg per day for most adults, and sets the tolerable upper limit for B-6 at 100 mg per day, but supplements often exceed that amount. (A 5-Hour ENERGY shot contains 40 mg of B-6.)
Ginkgo Biloba
Ginkgo biloba has been a favorite traditional herbal medicine for thousands of years, even though it’s not on the FDA’s GRAS list of safe ingredients. It’s taken to enhance memory and improve circulation. It can interact with other drugs and cause unwanted side effects, especially with anti-depressant medications and blood thinners. Energy drinks generally contain too small an amount to be of benefit.
L-Carnitine
L-Carnitine, a nutrient synthesized by amino acids in the body, converts food into energy, and helps move fat into cells to burn as energy. Some studies suggest it boosts metabolism, energy levels, and athletic endurance, but research is not conclusive. Most people on a normal diet produce adequate amounts, but physical stress may reduce available L-carnitine. It may cause gastrointestinal distress in some people.
Bottom line: Some of these ingredients may provide health or performance benefits, but probably not in the amounts found in energy drinks. People with health conditions or on medications should consult a doctor before consuming these substances.