Scan the label on an energy drink or energy shot, and you’ll likely see guarana: an ingredient twice as caffeinated as coffee, and a natural product of the Amazon. For centuries, natives there have used it medicinally, to suppress appetite, and for extending physical endurance.
Scan the label on an energy drink or energy shot, and you’ll likely see guarana: an ingredient twice as caffeinated as coffee, and a natural product of the Amazon. For centuries, natives there have used it medicinally, to suppress appetite, and for extending physical endurance.
What is guarana? The substance hails from the seeds of the guaraná plant, hence the name. Guaranine is the term for the caffeinated element in guarana, which is chemically identical to caffeine in coffee, tea and chocolate.
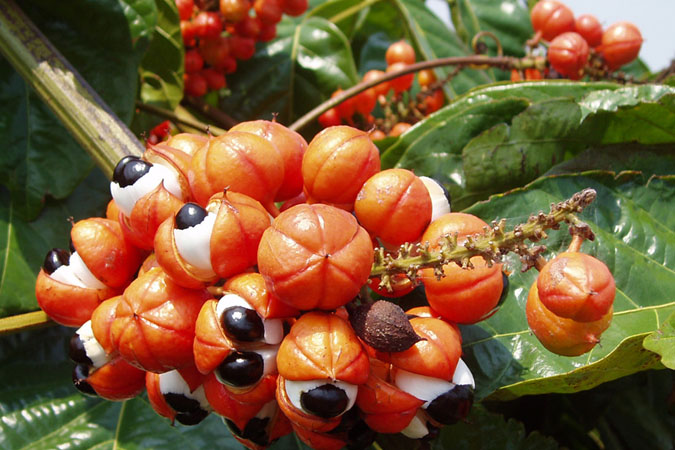
Where does guarana come from? Native to the Amazon basin, guaraná vines bear clumps of grape-size, Christmas-red berries and can climb as tall as 35 to 40 feet. When the three-sided guaraná fruits ripen, the capsule splits to reveal a black seed poking out of a white aril – they look like arm-length clusters of Muppet eyes. (Native legends say that the first guaraná plant sprouted from the eye of an infant god.) Native tribes have harvested guarana for centuries. The seeds are dried, ground, and brewed into tea or processed into an extract. Brazil is the leading supplier of guarana extract and powder, which are added to foods and beverages as a caffeine-boost.
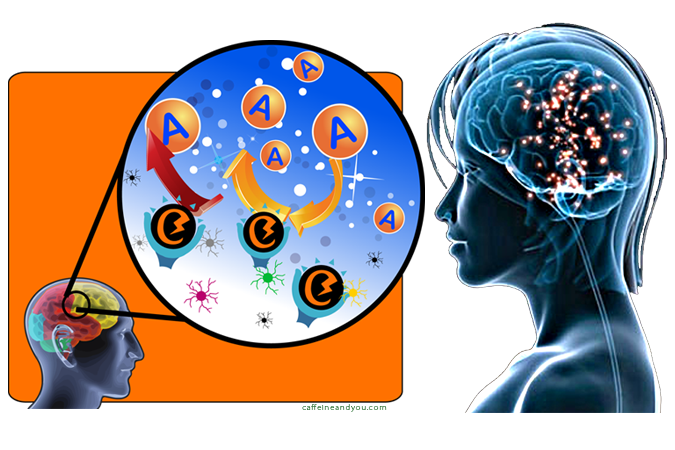
How much caffeine does guarana yield? Guarana seeds are twice as caffeinated as coffee beans, about 4% caffeine by weight (coffee has 1-2% caffeine). But it’s difficult to know how much guarana a product contains. Like coffee and tea, guarana is naturally caffeinated, so U.S. regulations do not require the amount of guarana to be listed. If caffeine is listed separately, it typically does not include the extra caffeine that comes from guarana or guaranine.
What else does guarana contain? Guarana also contains the caffeine-related stimulants theobromine and theophylline. Some studies show guarana yields antioxidant effects. It’s classified as GRAS, generally recognized as safe, by the U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA).
For more about guarana, check out:
Children of Guarana: Tribe, Legend, Plant
Guarana Soda: Brazil’s National Buzz
Return to: